Repetition Attenuates the Influence of Recency on Recognition Memory: Behavioral and Electrophysiological Evidence
Abstract
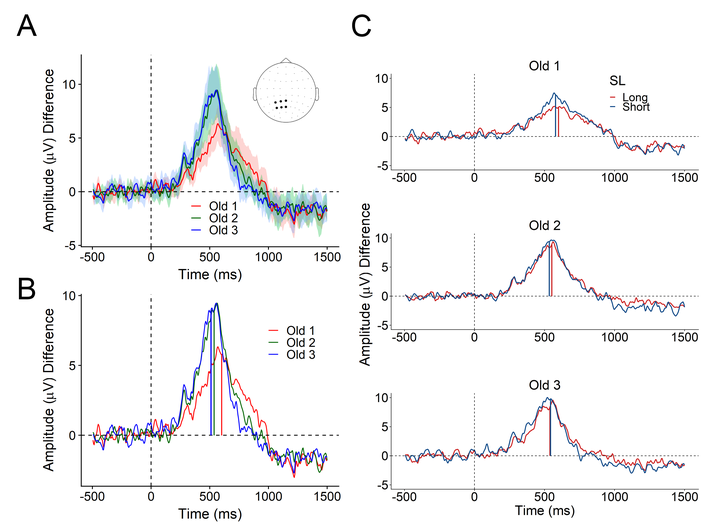
Studies of recognition memory often demonstrate a recency effect on behavioral performance, whereby response times (RTs) are faster for stimuli that were previously presented recently as opposed to more remotely in the past. One account of this relationship between performance and presentation lag posits that memories are accessed by serially searching backwards in time, such that RT indicates the self-terminating moment of such a process. Here, we investigated the conditions under which this serial search gives way to more efficient means of retrieving memories. Event-related potentials (ERPs) were recorded during a continuous recognition task in which subjects made binary old/new judgments to stimuli that were each presented up to four times across a range of lags. Stimulus repetition and shorter presentation lag both gave rise to speeded RTs, consistent with previous findings, and we novelly extend these effects to a robust latency measure of the left parietal ERP correlate of retrieval success. Importantly, the relationship between repetition and recency was further elucidated, such that repetition attenuated lag-related differences that were initially present in both the behavioral and neural latency data. These findings are consistent with the idea that an effortful search through recent memory can quickly be abandoned in favor of relying on more efficient ‘time-independent’ cognitive processes or neural signals.